Vaccine Types
Influenza
Why is it important?
Flu is especially serious for young children. Each year an average of 20,000 children under age five are hospitalized because of flu complications. Some children, including those with chronic health conditions like asthma and diabetes, are especially at risk for serious flu complications. Pregnant women, adults with chronic health conditions and people 65 years and older are also at increased risk of flu. However, even previously healthy children can become seriously ill from seasonal influenza.
While practicing healthy habits such as hand washing and covering your cough are important measures for preventing the spread of illness, the best way to prevent influenza is to get a flu vaccine as soon as it becomes available (usually in October). Flu vaccines are offered by many doctor’s offices, clinics, health departments, schools and pharmacies.
To track where flu is occurring in Colorado, the United States and worldwide, and to view previous seasonal flu reports, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s flu surveillance page.
Vaccine Recommendations
This season, the CDC recommends everyone six months of age and older get the 2015-2016 flu vaccine, which will protect against the three different influenza viruses that research indicates will be most common during the season. This includes an influenza A (H1N1) virus, an influenza A (H3N2) virus, and an influenza B virus. Some of the 2015-2016 flu vaccines will be quadrivalent, protecting against a second strain of the influenza B virus. This will provide greater protection against the virus.
Children may need two doses of influenza vaccine. Your child’s health care provider can tell you whether two doses are recommended for your child. The 2015-2016 influenza vaccine is available in a shot and a nasal spray (ages 2-49 years).
It is also highly recommend that people who care for or live with others who are at high risk (i.e. infants, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with certain illnesses) get vaccinated annually to reduce the chance of spreading flu to their family, patients or community.
For flu and flu vaccine information specific to the current flu season, visit the CDC’s What You Should Know for the 2015-2016 Influenza Season webpage.
Side Effects
Serious problems from influenza vaccine are very rare. In a study, examining the effects of both the inactivated influenza vaccine (shot) and the live, attenuated influenza vaccine (nose spray), with more than 250,000 children under age 18, investigators did not identify risk for any clinically important serious reactions from the vaccine. The viruses in the nasal spray vaccine have been greatly weakened, and the viruses in the influenza shot have been killed, so you cannot get influenza from these vaccines.
Influenza vaccines can cause mild problems. These include:
- Soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given
- Sore throat
- Hoarseness, sore or red eyes, cough, itchiness
- Fever
- Aches
Slightly more reports of mild fevers, runny nose and nasal congestion occurred after the first dose of the nasal spray. If these problems occur, they usually begin soon after the vaccine and last 1 to 2 days.
Influenza
Influenza
Influenza (flu) is a highly contagious viral upper respiratory illness. Flu may be complicated by other risk factors, including pneumonia. [+] more
|
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) affects the liver and is primarily spread through blood and bodily fluids. Acute HBV infection can lead to chronic HBV and liver damage. [+] more
|
Polio
Polio
Poliomyselitis (polio) is an extremely contagious viral infection that affects the nerve cells of the brain stem and spinal cord and can lead to paralysis. [+] more
|
Diphtheria
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a bacterial respiratory illness that causes a thick covering in the back of the throat, leading to breathing problems, paralysis, or heart failure. [+] more
|
Rotavirus
Rotavirus
Rotavirus is a viral infection of the digestive track, and is the most common cause of severe diarrhea and vomiting in infants and young children. [+] more
|
Pneumococcal
Pneumococcal
Pneumococcal bacteria live in noses and throats of people of all ages. Pneumococcus can infect the middle ear, sinuses, lungs, central nervous system and bloodstream. [+] more
|
Measles
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral respiratory infection that causes a total-body skin rash and flu-like symptoms. [+] more
|
Mumps
Mumps
Mumps is a highly contagious viral infection that can affect many parts of the body. The hallmark sign of mumps is swelling of the salivary glands. [+] more
|
Rubella
Rubella
Rubella (German measles) is a contagious viral disease that can cause fever, rash, swollen glands and arthritis. Infection during pregnancy can lead to birth defects. [+] more
|
Tetanus
Tetanus
Tetanus (Lockjaw) is a bacterial infection that affects the nervous system and causes painful tightening of the muscles all over the body. It is spread through contact with contaminated surfaces. [+] more
|
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)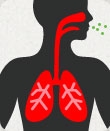
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) is a highly contagious bacterial respiratory disease. Pertussis causes violent coughing spells that make it hard to eat, drink or breathe, and is especially severe in young infants. [+] more
|
Chickenpox
Chickenpox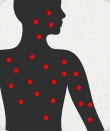
Varicella (Chickenpox) is a highly contagious viral infection characterized by a blistering rash that can cover the entire body. Complications include skin infections, pneumonia and brain swelling. [+] more
|
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A (HAV) virus attacks the liver, and is spread through stool of an infected person by direct contact or by contaminated food or drink. [+] more
|
Meningococcal
Meningococcal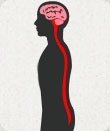
Meningococcal disease is a severe bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (bacterial meningitis) and blood poisoning (septicemia), and requires immediate medical attention. [+] more
|
Hib
Hib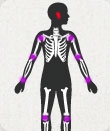
Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib) bacterium can infect a child’s skin, joints, bones and ears. Hib can lead to a variety of infections including pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis. [+] more
|
HPV
HPV
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States. About 40 types of HPV can infect the genital areas of males and females. A few types can lead to cervical and other cancers. [+] more
|