Vaccine Types

Tetanus
What is it?
Tetanus (Lockjaw) is a serious, often deadly, disease that causes painful tightening of the muscles, usually all over the body. It can lead to “locking” of the jaw so the victim cannot open his mouth or swallow. It is spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Why is it important?
Unlike most vaccine-preventable diseases, tetanus is not a disease that you catch from someone else. The tetanus bacteria live in soil and usually enter the body through a scrape or cut. Once tetanus has spread throughout the body, the death rate is about 30%. Vaccination is the best way to protect against tetanus.
Tetanus is extremely dangerous for pregnant women and their babies. When mothers are not immune, tetanus kills up to 200,000 babies a year. This contributes to infant and maternal deaths in developing countries.
Progress
Widespread use of the tetanus vaccine led to a decrease in cases in the U.S., from 500 cases in the 1940s to about 50 cases each year.
Vaccine Recommendations
With the DTaP vaccine you prevent 3 diseases with 1 shot: diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Children should get 5 doses of DTaP vaccine, one dose at each of the following ages:
- 2 months
- 4 months
- 6 months
- 15-18 months
- 4-6 years
Anyone who comes in contact with a baby – parents, grandparents, caregivers, siblings, plus extended family and friends – should receive the adult form of the vaccine (Tdap) to help shield or "cocoon" newborns from whooping cough. It is also recommended that pregnant women receive a Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy between weeks 27 and 36 to benefit mother and baby. When a mom-to-be is vaccinated, she passes disease-fighting antibodies onto her baby to help protect him or her after birth.
Side Effects
While the risk of DTaP vaccine causing serious allergic reaction is very small (about 1 in 1 million) common side effects of this vaccine may include:
- Fever (up to about 1 child in 4)
- Redness or swelling where the shot was given (up to about 1 child in 4)
- Soreness or tenderness where the shot was given (up to about 1 child in 4)
Other mild problems include:
- Fussiness (up to about 1 child in 3)
- Tiredness or poor appetite (up to about 1 child in 10)
- Vomiting (up to about 1 child in 50)
These problems generally occur 1-3 days after the shot.
Moderate problems may include seizure (1 in 14,000), crying for 3+ hours (1 in 1,000), or high fever (1 in 16,000).
Influenza
Influenza
Influenza (flu) is a highly contagious viral upper respiratory illness. Flu may be complicated by other risk factors, including pneumonia. [+] more
|
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) affects the liver and is primarily spread through blood and bodily fluids. Acute HBV infection can lead to chronic HBV and liver damage. [+] more
|
Polio
Polio
Poliomyselitis (polio) is an extremely contagious viral infection that affects the nerve cells of the brain stem and spinal cord and can lead to paralysis. [+] more
|
Diphtheria
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a bacterial respiratory illness that causes a thick covering in the back of the throat, leading to breathing problems, paralysis, or heart failure. [+] more
|
Rotavirus
Rotavirus
Rotavirus is a viral infection of the digestive track, and is the most common cause of severe diarrhea and vomiting in infants and young children. [+] more
|
Pneumococcal
Pneumococcal
Pneumococcal bacteria live in noses and throats of people of all ages. Pneumococcus can infect the middle ear, sinuses, lungs, central nervous system and bloodstream. [+] more
|
Measles
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral respiratory infection that causes a total-body skin rash and flu-like symptoms. [+] more
|
Mumps
Mumps
Mumps is a highly contagious viral infection that can affect many parts of the body. The hallmark sign of mumps is swelling of the salivary glands. [+] more
|
Rubella
Rubella
Rubella (German measles) is a contagious viral disease that can cause fever, rash, swollen glands and arthritis. Infection during pregnancy can lead to birth defects. [+] more
|
Tetanus
Tetanus
Tetanus (Lockjaw) is a bacterial infection that affects the nervous system and causes painful tightening of the muscles all over the body. It is spread through contact with contaminated surfaces. [+] more
|
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)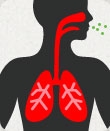
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) is a highly contagious bacterial respiratory disease. Pertussis causes violent coughing spells that make it hard to eat, drink or breathe, and is especially severe in young infants. [+] more
|
Chickenpox
Chickenpox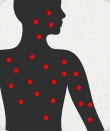
Varicella (Chickenpox) is a highly contagious viral infection characterized by a blistering rash that can cover the entire body. Complications include skin infections, pneumonia and brain swelling. [+] more
|
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A (HAV) virus attacks the liver, and is spread through stool of an infected person by direct contact or by contaminated food or drink. [+] more
|
Meningococcal
Meningococcal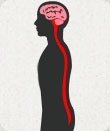
Meningococcal disease is a severe bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (bacterial meningitis) and blood poisoning (septicemia), and requires immediate medical attention. [+] more
|
Hib
Hib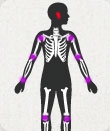
Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib) bacterium can infect a child’s skin, joints, bones and ears. Hib can lead to a variety of infections including pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis. [+] more
|
HPV
HPV
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States. About 40 types of HPV can infect the genital areas of males and females. A few types can lead to cervical and other cancers. [+] more
|